Snowflake
Snowflake is a cloud data warehouse platform. OpenRouter can stream traces directly to your Snowflake database for custom analytics, long-term storage, and business intelligence.
Step 1: Create the traces table
Before connecting OpenRouter, create the OPENROUTER_TRACES table in your Snowflake database. You can find the exact SQL in the OpenRouter dashboard when configuring the destination:
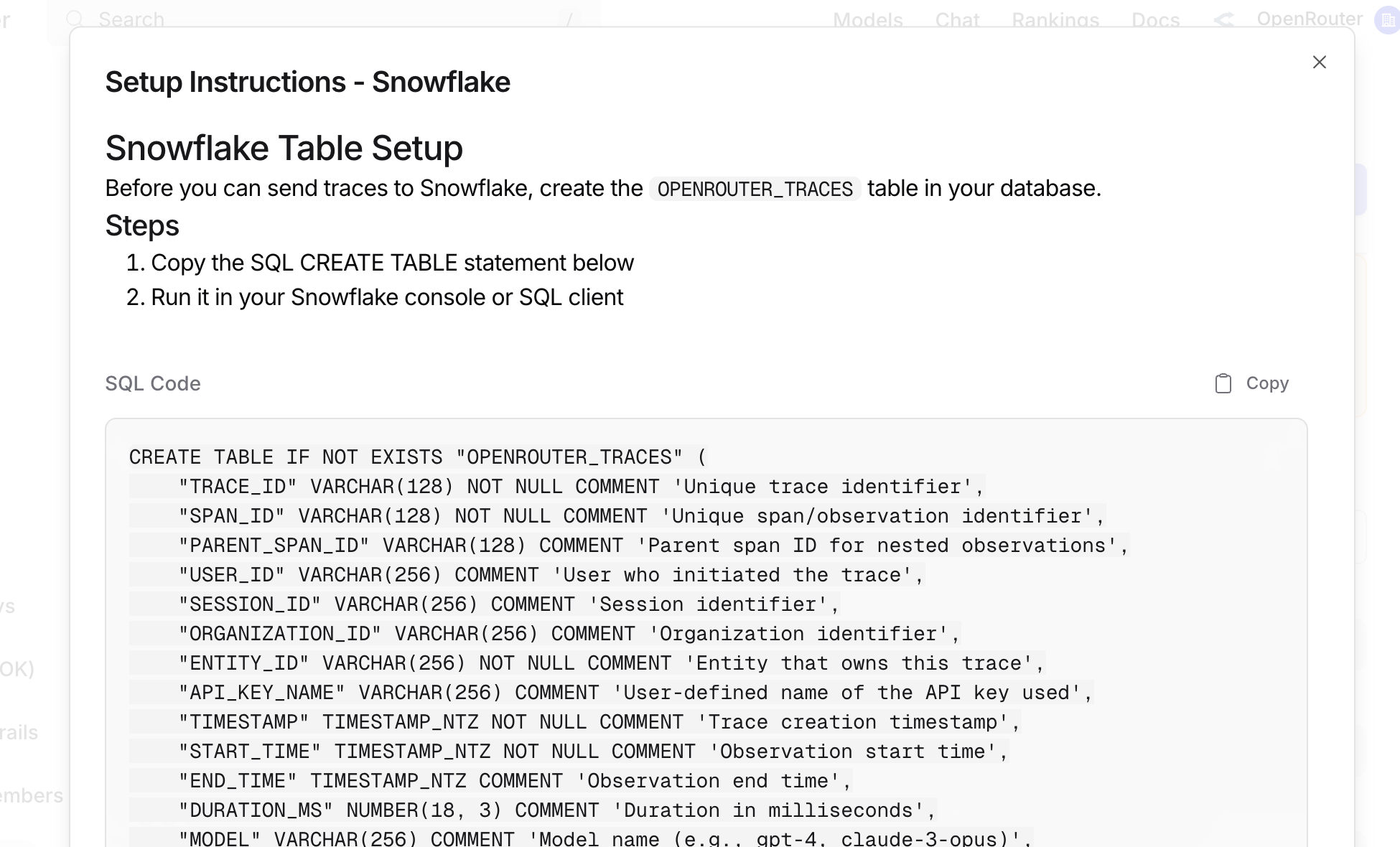
Step 2: Create access credentials
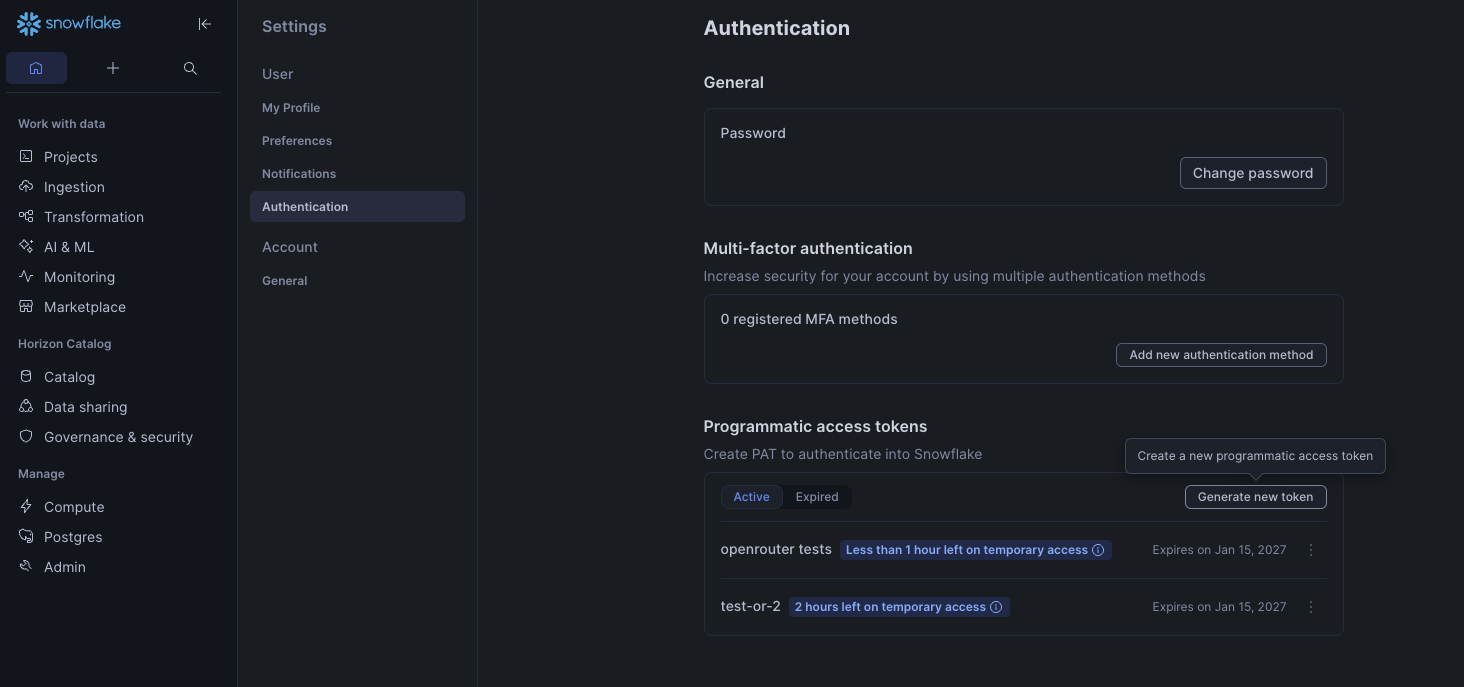
Generate a Programmatic Access Token with ACCOUNTADMIN permissions in the Snowflake UI under Settings > Authentication.
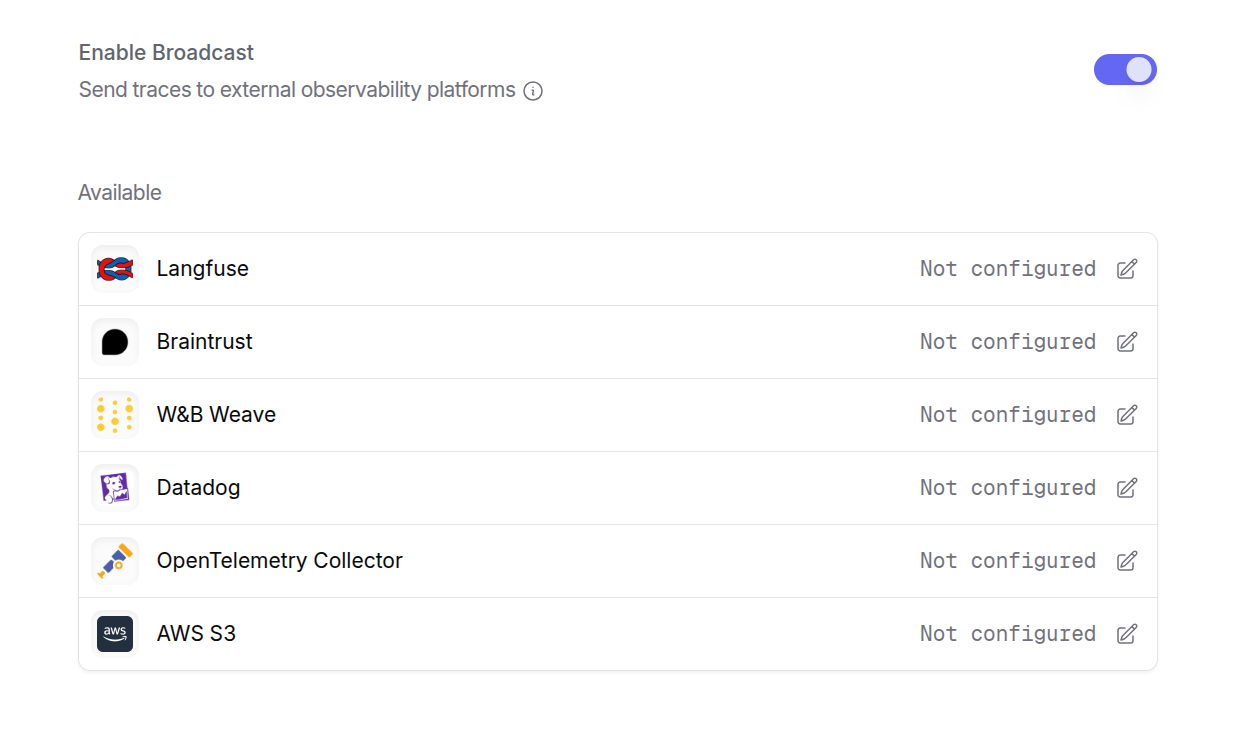
Step 3: Enable Broadcast in OpenRouter
Go to Settings > Broadcast and toggle Enable Broadcast.
Step 4: Configure Snowflake
Click the edit icon next to Snowflake and enter:
- Account: Your Snowflake account identifier (e.g.,
eac52885.us-east-1). You can find your account region and your account number at the end of your Snowflake instance’s URL: https://app.snowflake.com/us-east-1/eac52885; together these make your account identifier. - Token: Your Programmatic Access Token.
- Database: Target database name (default:
SNOWFLAKE_LEARNING_DB). - Schema: Target schema name (default:
PUBLIC). - Table: Table name (default:
OPENROUTER_TRACES). - Warehouse: Compute warehouse name (default:
COMPUTE_WH).
Step 5: Test and save
Click Test Connection to verify the setup. The configuration only saves if the test passes.
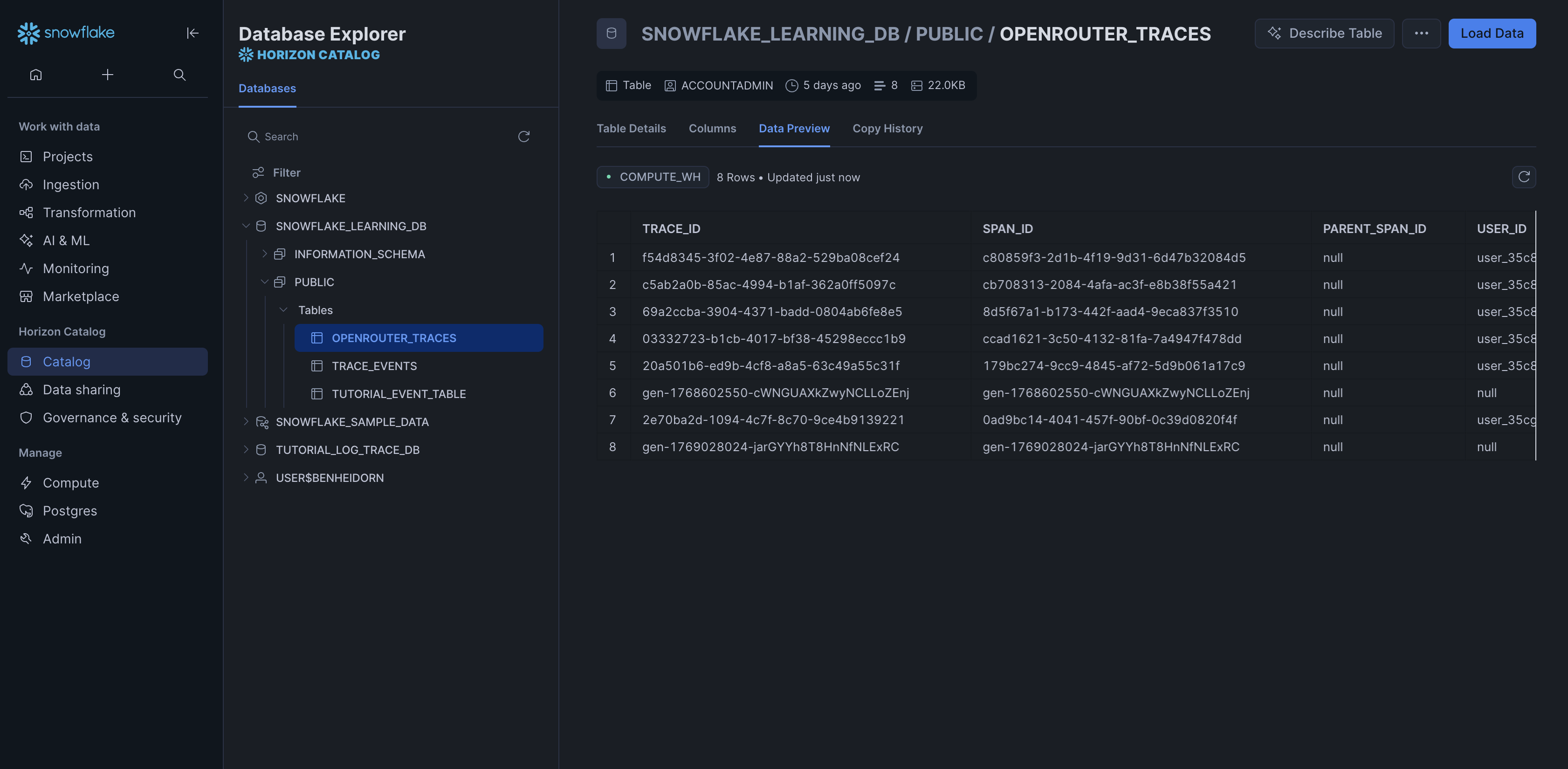
Step 6: Send a test trace
Make an API request through OpenRouter and query your Snowflake table to verify the trace was received.
Example queries
Cost analysis by model
User activity analysis
Error analysis
Provider performance comparison
Usage by API key
Accessing VARIANT columns
Parsing input messages
Schema design
Typed columns
The schema extracts commonly-queried fields as typed columns for efficient filtering and aggregation:
- Identifiers: TRACE_ID, USER_ID, SESSION_ID, etc.
- Timestamps: For time-series analysis
- Model Info: For cost and performance analysis
- Metrics: Tokens and costs for billing
VARIANT columns
Less commonly-accessed and variable-structure data is stored in VARIANT columns:
- ATTRIBUTES: Full OTEL attribute set
- INPUT/OUTPUT: Variable message structures
- METADATA: User-defined key-values
- MODEL_PARAMETERS: Model-specific configurations
This design balances query performance with schema flexibility and storage efficiency.